It is feasible for a single-practitioner podiatry practice to add weight bearing CT (WBCT) imaging and realize economical…

WBCT Indications Series: Syndesmosis
Syndesmosis
A syndesmotic ankle sprain, also known as high ankle sprain, is an injury to one or more of the ligaments comprising the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis.
A weight bearing CT scan can:
- Provide increased sensitivity and specificity over radiographs.
- Differentiate pathology from natural variability in patient anatomy via contralateral comparison to uninjured ankle as internal control1.
- Help detect subtle syndesmosis injuries.
- Assess for instability, especially in cases with accompanying Weber B fractures2.
Diagnosis
If WB X-rays are indeterminate after clinical exam, order a bilateral WBCT. WBCT scans can also be used as an adjunct to an ankle MRI to correlate anatomic abnormalities with functional instability.
Treatment Planning
In cases of equivocal syndesmotic injuries, the gold standard for the diagnosis of syndesmotic injuries has been ankle arthroscopy. However, bilateral WBCT scans may be useful to decrease uncertainty and avoid this invasive procedure.
Comparing the syndesmotic area (Case #1) between the injured and uninjured sides can help to predict subtle syndesmotic instability. Patients with differences in syndesmotic area between the injured and uninjured sides are correlated with unstable syndesmotic injuries and may benefit from surgical stabilization3.
Plan revision surgery by better understanding the direction of the malreduction and comparing the amount of diastasis to the contralateral side.
Postoperative Assessment
For postoperative assessment of syndesmosis treatment, a WBCT can:
- Accurately detect and quantify malreduction4.
- Identify and quantify diastasis at the syndesmosiswith functional instability.
Subtle Syndesmotic Injury
24 yo lacrosse player who presented with concern for a left high ankle sprain. X-rays were non-diagnostic.
WBCT scan demonstrated increased widening of the syndesmotic area on the injured side.
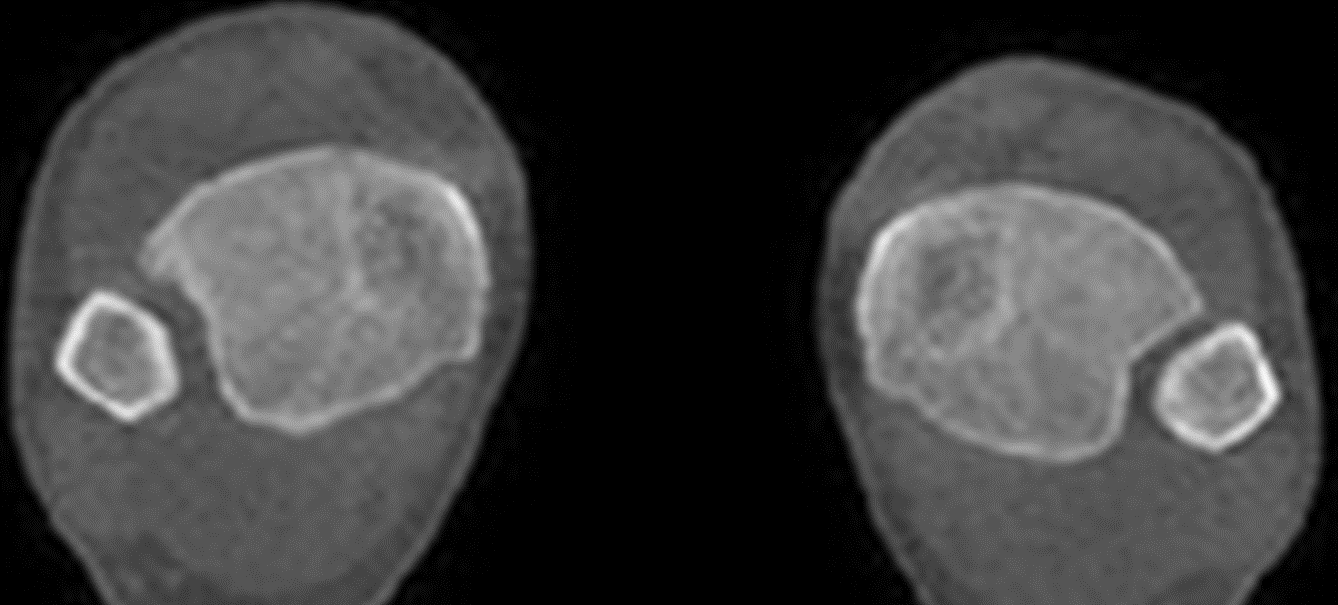
WBCT scan showed a subtle syndesmosis injury (left) when compared to the uninjured side (right).
Resulting treatment was open reduction and repair of the syndesmosis with flexible fixation.
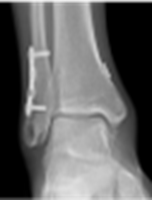
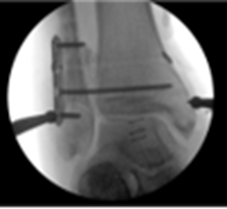
Syndesmotic Malreduction
60 yo male who presented with persistent left ankle pain after open reduction internal fixation at an outside institution. (left)
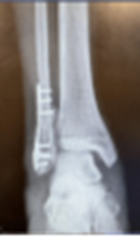
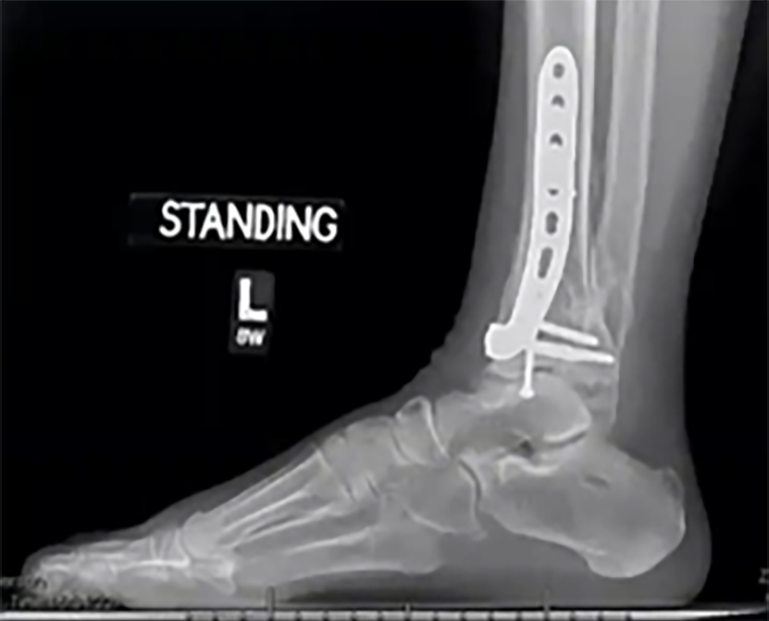
WBCT showed syndesmotic malreduction with posterior widening of the syndesmosis. (right)
Resulting treatment plan was removal of hardware with revision ORIF of the syndesmosis with rigid and flexible fixation.
Click Here to get direct links to the latest studies using WBCT scans.

Dr. Kent Ellington, MD
Dr. Kent Ellington, an OrthoCarolina Foot and Ankle Surgeon, has more than two decades of research experience in his field and is a well-respected name in diagnosis and treatment of below-the-knee conditions.
(1) Hagemeijer NC, Chang SH, Abdelaziz ME, Casey JC, Waryasz GR, Guss D, DiGiovanni CW. Range of Normal and Abnormal Syndesmotic Measurements Using Weightbearing CT. Foot Ankle Int. 2019 Dec;40(12):1430-1437. doi: 10.1177/1071100719866831. Epub 2019 Aug 23. PMID: 31442094.
(2) Bhimani, Rohan MD, MBA; Ashkani-Esfahani, Soheil MD; Lubberts, Bart MD, PhD; Kaiser, Philip MD; Kerkhoffs, Gino M.M.J. MD; Waryasz, Gregory MD; DiGiovanni, Christopher W. MD; Guss, Daniel MD, MBA. Utility of WBCT to Diagnose Syndesmotic Instability in Patients With Weber B Lateral Malleolar Fractures. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons: February 1, 2022 – Volume 30 – Issue 3 – p e423-e433
doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-21-00566
(3) Weightbearing Cone-Beam Computed Tomography of Acute Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries RSS Download PDF Andres del Rio MBBS, FRANZCR, Samuel M. Bewsher MBBS, FRACS, Sasha Roshan-Zamir MBBS, FRACS, Julie TateBSc, Maggie Eden BSc, Robert Gotmaker MBBS, FANZCA, Otis Wang MBBS, FRACS, Harvinder S. Bedi MBBS, FRACS and Andrew H. Rotstein MBBS, FRANZCR Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, The, 2020-03-01, Volume 59, Issue 2, Pages 258-263, Copyright © 2019 the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons
(4) de Cesar Netto C, Kwon JY, Mansur NS, et al. Syndesmotic Malreduction Assessment using Three-Dimensional Distance Mapping: A Cadaveric WBCT Study. Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics. 2022;7(4). doi:10.1177/2473011421S00646




