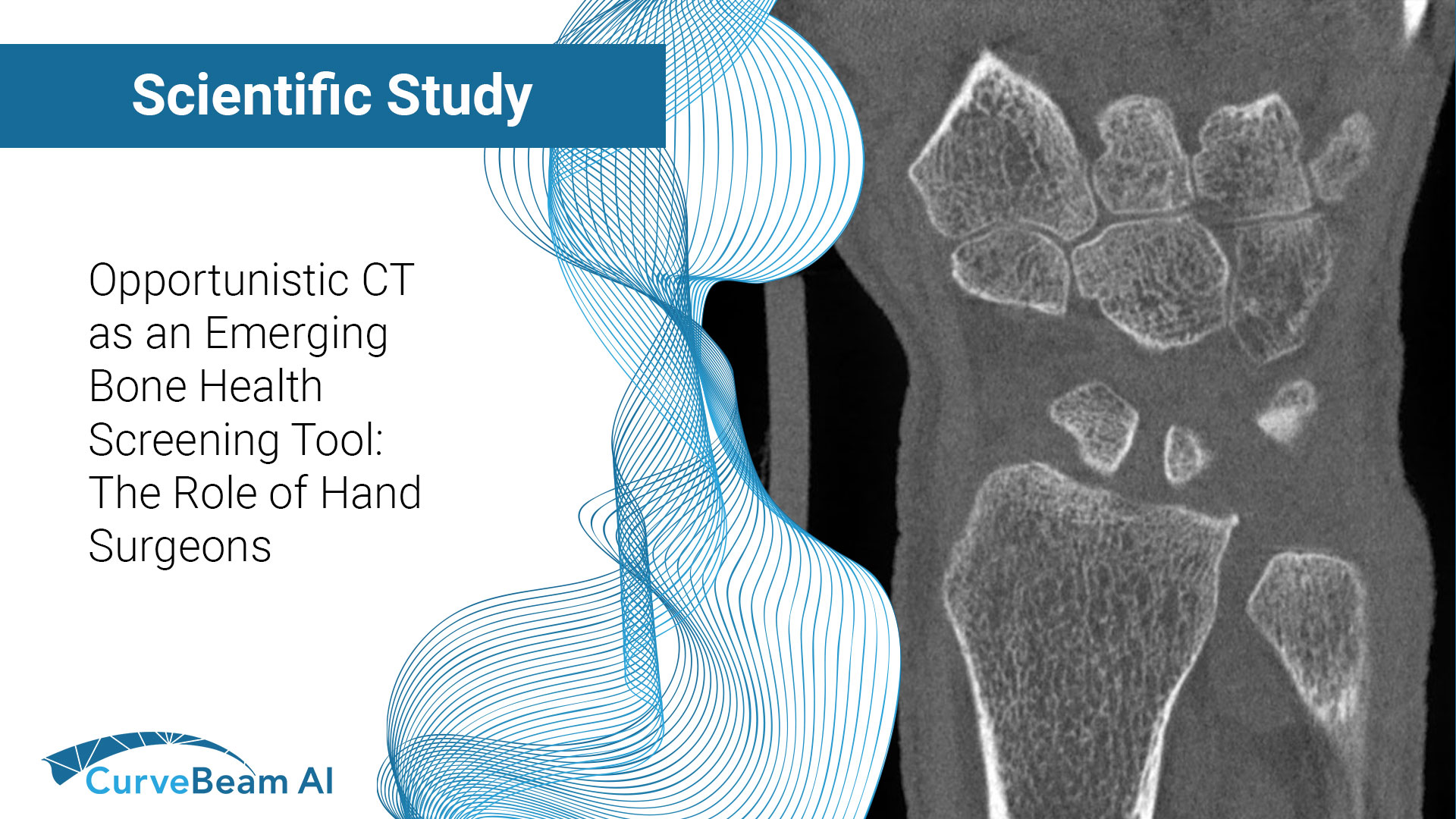
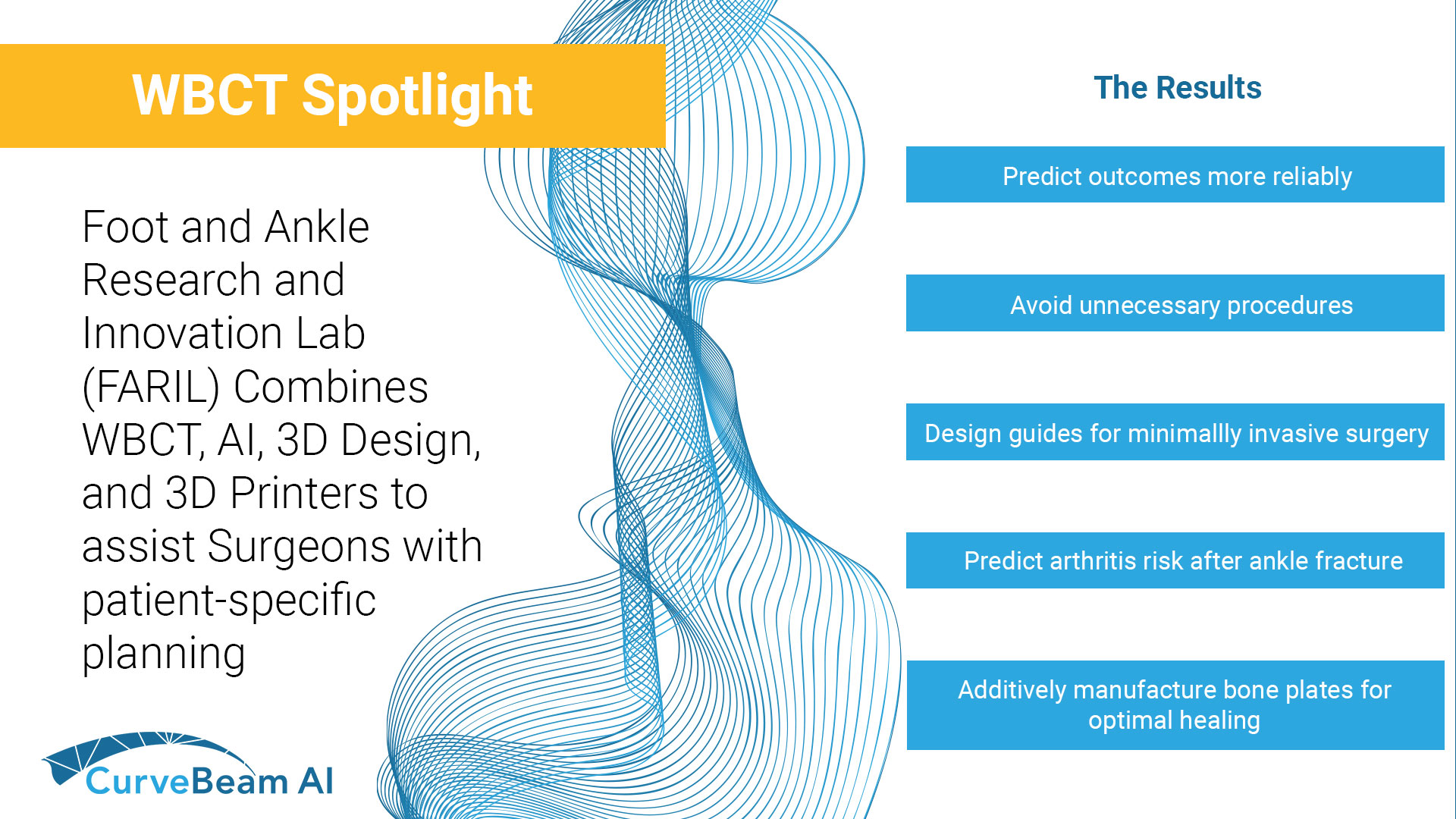
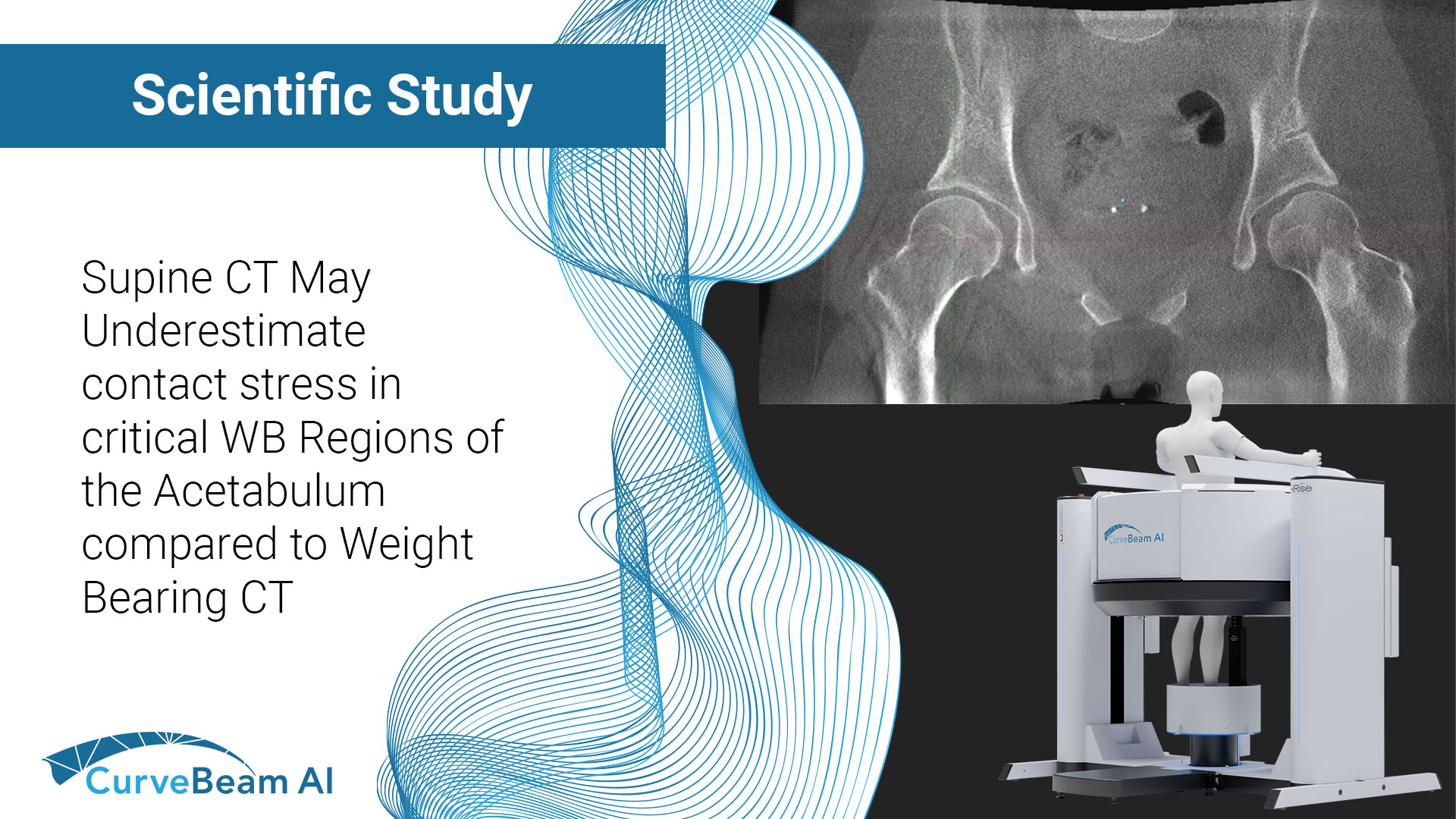
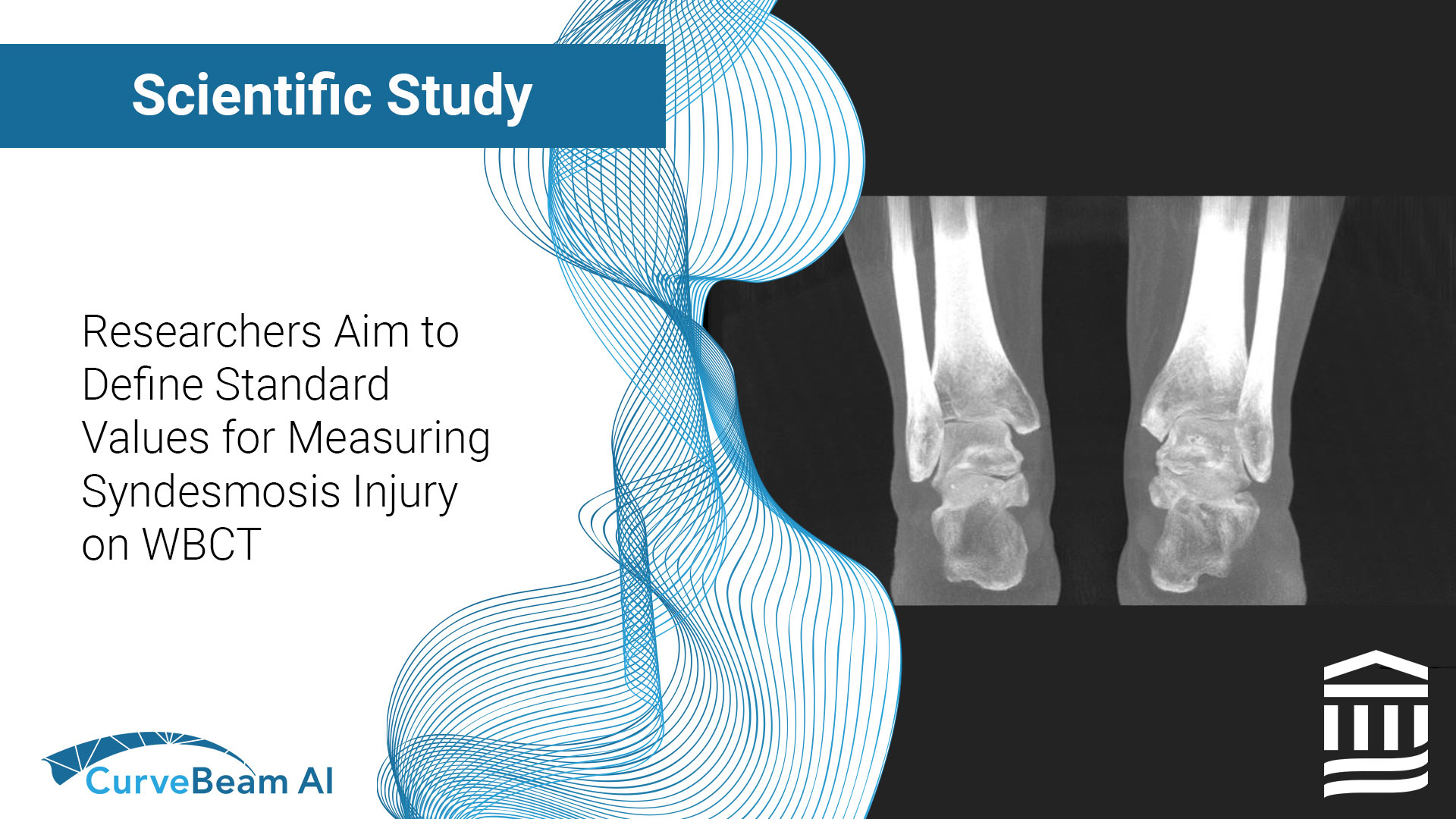
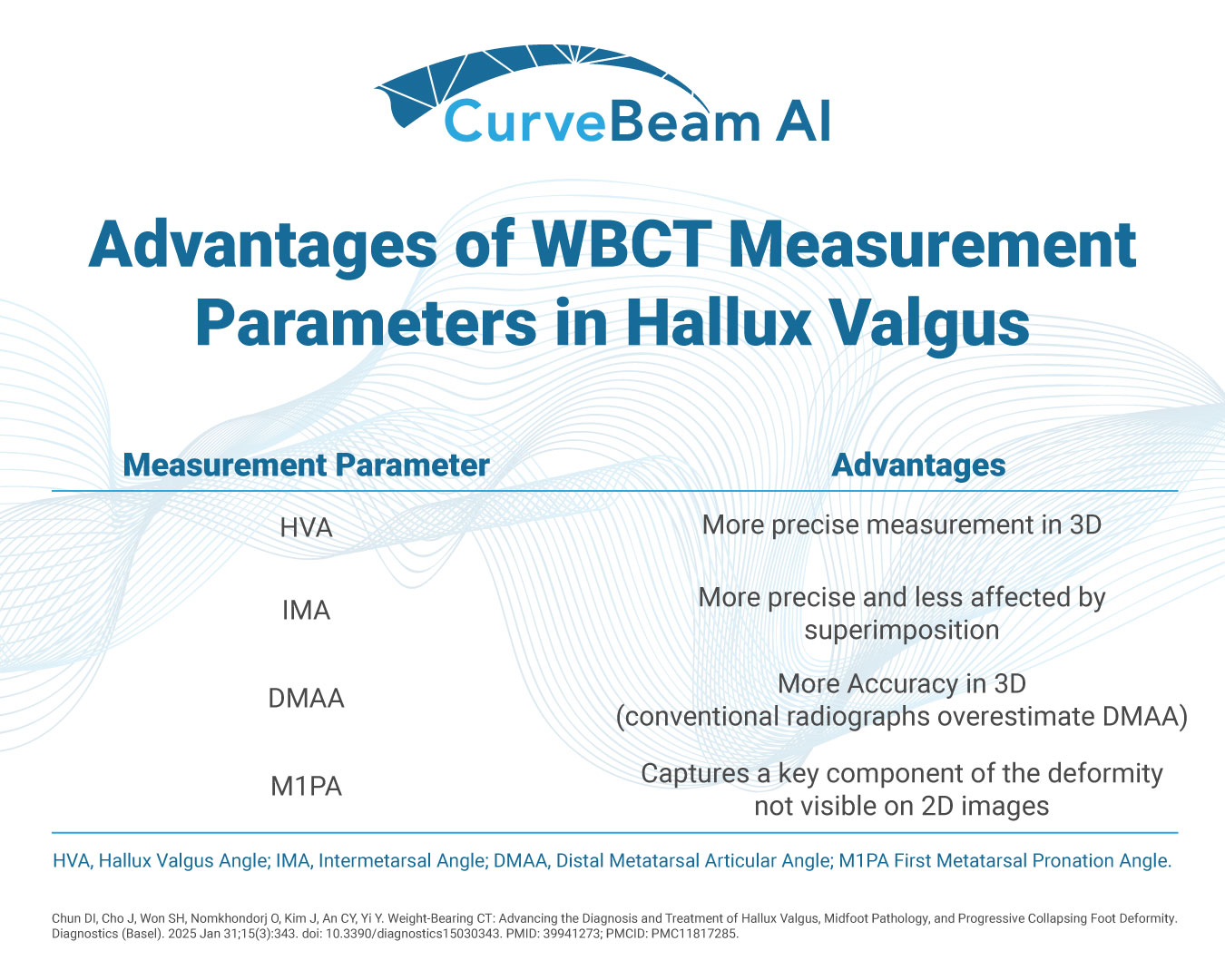
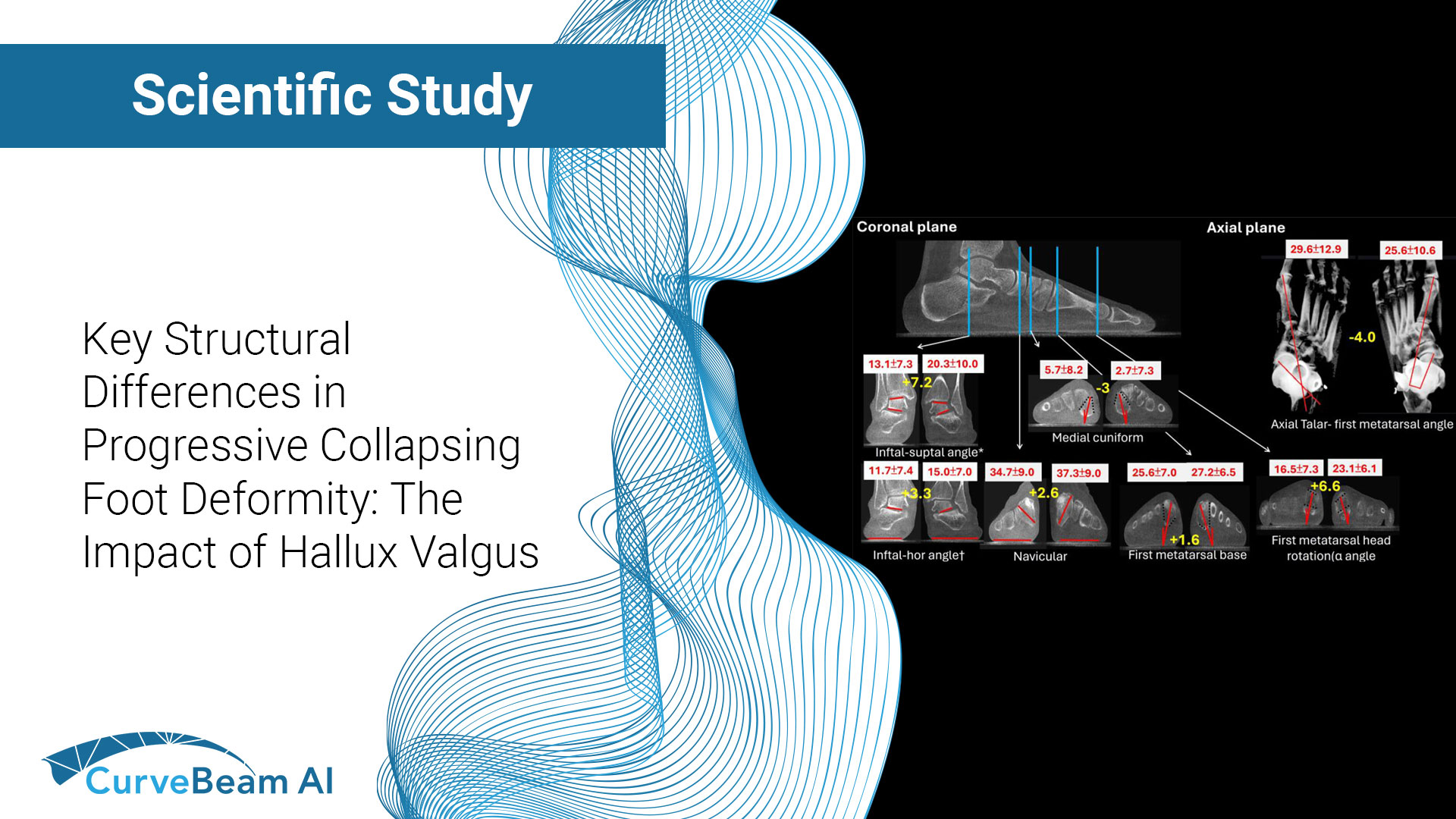
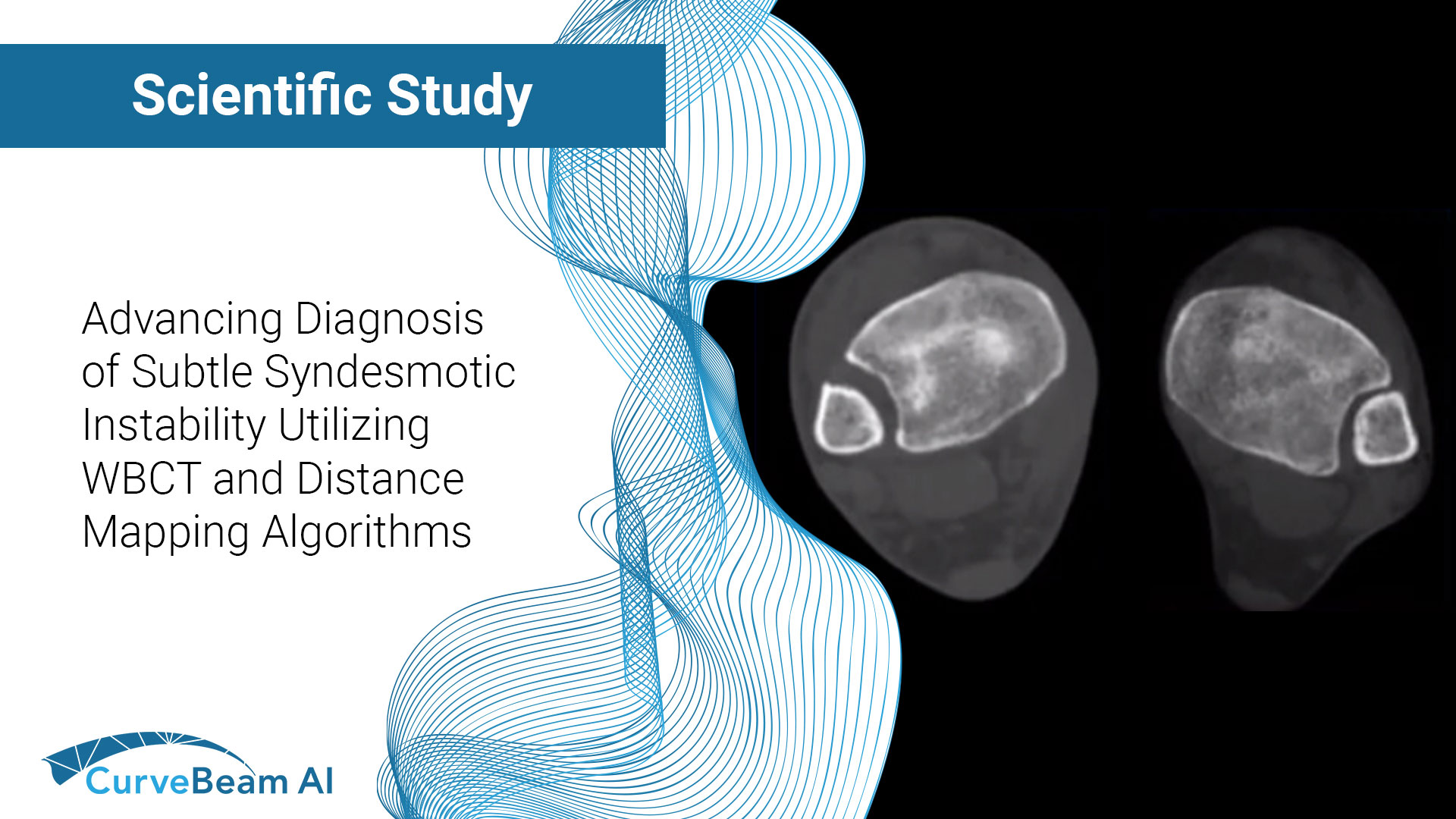
Sub-Millimeter Accuracy in Weight-Bearing Orthopedic Imaging
Orthopedic decision-making depends on accurate representation of anatomy—particularly when joint alignment and bone relationships change under load. Conventional supine imaging can obscure these functional differences, creating uncertainty in assessment and surgical planning. A recent internal investigation evaluated whether weight-bearing cone…